On-site investigation and assessment as and when required.
Formulation of a proper test plan.

Hazard and risk identification.

Scientific interpretation of data and formal reporting of results.

Pre-loss and loss recommendations can be aloss-adjusting tool for assessors and claims investigators.

Training courses for assessors and claims investigators.
Lorca Consulting performs analysis on the following damages:

Fire damage that occurs without criminal intent.

Smoke and Water Damage to property.
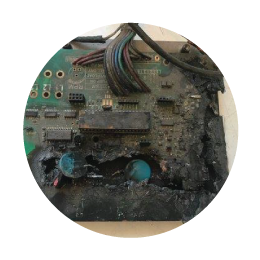
Power Surge Analysis (lightning vs surge).

Battery and Solar System failure analysis.

Product Failure and Root Cause Analysis.
You may be an insurer that wants to determine if a claim is factual, you may be a brokerage that wants fair compensation
for your client, or you may be a claimant that feels that your claim was inadequately assessed.
Lorca Consulting is ready to assist.
Several types of analysis may be undertaken that fall within the broader framework of failure analysis. Below are a few types of analyses that may be conducted depending on the context of a given failure:
Several types of analysis may be undertaken that fall within the broader framework of failure analysis.
Below are a few types of analyses that may be conducted depending on the context of a given failure:
Failure analysis is a systematic investigative procedure using the scientific method to identify the causes of a failure.
The Failure Analysis Society is the newest affiliate society from ASM International. Founded in 2016, this society is dedicated to advancing failure analysis’s vital role in the materials science industry.
ASM methodology is applied to conduct failure analysis where appropriate.
The Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) Process is followed. The FMEA methodology is based on a hierarchical, inductive approach to analysis.
Note: Testing methods may be destructive or non-destructive (context-dependent)
• Physical investigation [X-ray fluorescence – XRF], X-ray diffraction [XRD], RAMAN spectroscopy
• Chemical analysis (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy [FTIR], inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy [ICP-MS], total organic carbon [TOC], gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy [GC-MS]
• Wet chemical analysis (pH, ion identification, density)
• Thermal imaging
• UV analysis
• Microscopy (stereo) and scanning electron microscopy [SEM]
• Electronic testing